Xanthelasma FAQs
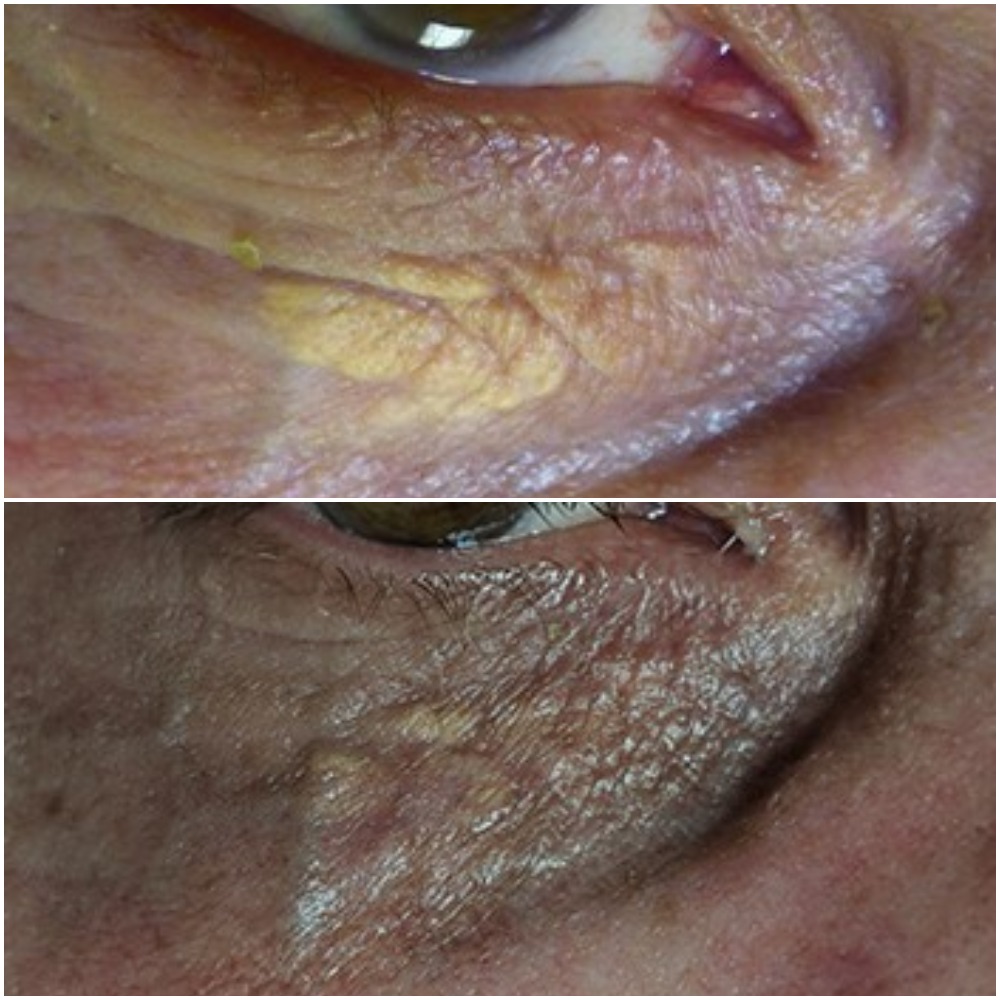
Xanthelasma are characterised as soft, yellowish, fatty deposits that form under the skin around the eyes. They are not harmful but can be an indicator of cholesterol issues so always get this checked by a doctor.
Cauterisation is the safest and fastest way to remove xanthelasma. We use ACP (an advanced form of electrolysis) that involves using a probe with a current emitted to the end of it, by tapping this against the xanthelasma it’s cauterised, causing the outer skin to harden up and fall off in the following days lightening the appearance of the xanthelasma. Usually only 1 treatment is needed, however for bigger xanthelasma an additional treatment is sometimes required. If you are prone to them, they may return. Top up treatments may be required every 1-2 years.
Xanthelasma are formed when deposits of cholesterol (lipid or fat) build up under the skin. While xanthelasma themselves are not harmful, they can be a sign of heart disease so it’s always best to have your cholesterol checked by a doctor if you develop them.
Lowering cholesterol may help to treat xanthelasma. Making positive changes to diet and lifestyle, such as stopping smoking and limiting alcohol consumption. In some cases they will not disappear on their own and treatment is needed to remove them. Cauterisation is the safest and fastest way to remove xanthelasma. We use ACP (an advanced form of electrolysis) that involves using a probe with a current emitted to the end of it, by tapping this against the xanthelasma it’s cauterised, causing the outer skin to harden up and fall off in the following days lightening the appearance of the xanthelasma.
Xanthelasma are formed when deposits of cholesterol (lipid or fat) build up under the skin. While xanthelasma themselves are not harmful, they can be a sign of heart disease so it’s always best to have your cholesterol checked by a doctor if you develop them.
ACP (an advanced form of electrolysis) involves using a probe with a current emitted to the end of it, by tapping this against the xanthelasma it’s cauterised, causing the outer skin to harden up and fall off in the following days lightening the appearance of the xanthelasma. Usually only 1 treatment is needed, however for bigger xanthelasma an additional treatment is sometimes required. If you are prone to them, they may return. Top up treatments may be required every 1-2 years.
Some higher strength salicylic acid can be used to reduce the appearance of xanthelasma, however as they are located around the eyes this can cause skin sensitivity. Professional treatment is recommended for the safest and fastest removal of xanthelasma.
Xanthelasma are characterised as soft, yellowish, fatty deposits that form under the skin around the eyes.
Half of the people with xanthelasma have high cholesterol levels. Healthcare providers usually see these levels in people with the kind of high cholesterol you get from your parents or some liver diseases. However, the other 50% of people with xanthelasmas don’t have high cholesterol.
Lowering cholesterol may help to treat xanthelasma. Making positive changes to diet and lifestyle, such as stopping smoking and limiting alcohol consumption.
Do get your cholesterol checked if you develop them
Don’t try to remove them yourself at home
Do avoid putting thick eye creams and vaseline around your eyes
Lowering cholesterol may help to prevent xanthelasma. Making positive changes to diet and lifestyle, such as stopping smoking and limiting alcohol consumption.
Prices will vary based upon your location, the quality of the machine being used and the experience of your practitioner. Head to our price list to see pricing of our ACP blemish removal treatment which is the most commonly recommended treatment for xanthelasma.